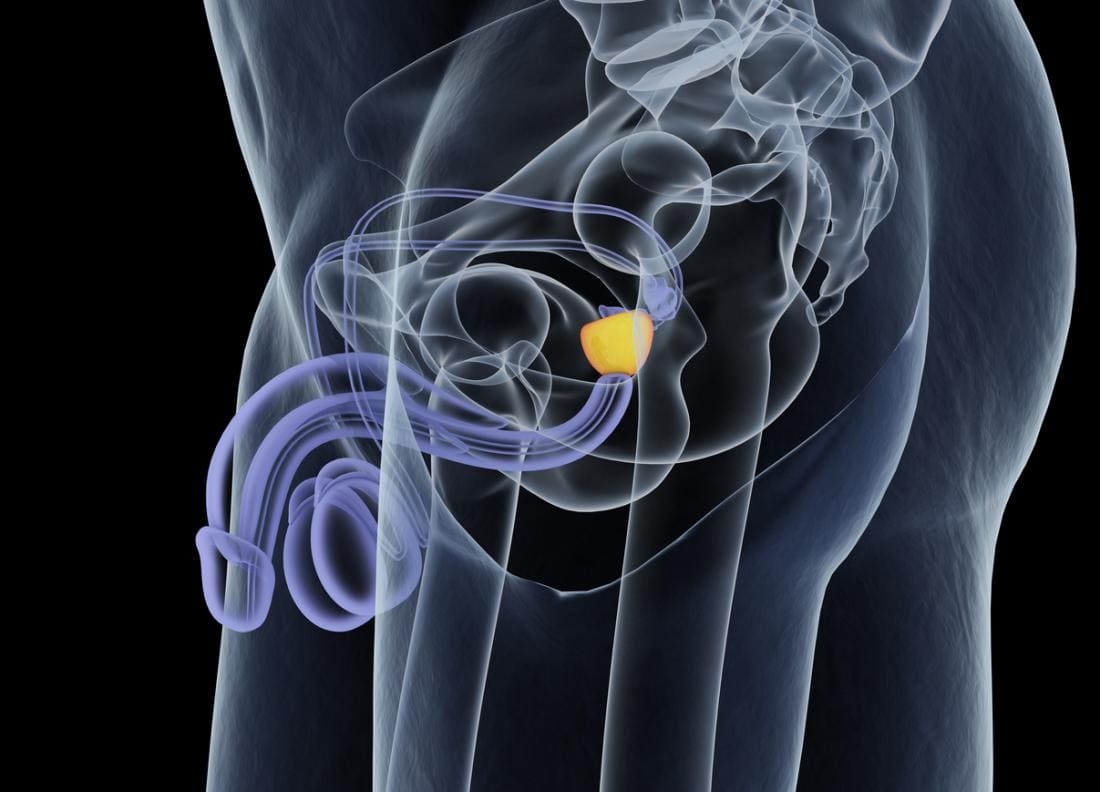
Prostate Infection
It is an inflammation of the prostate gland. It can be caused by bacteria or other microorganisms. There are two types: acute and chronic. Acute prostatitis starts suddenly and is severe. Chronic prostatitis is long-lasting and its symptoms are mild. Prostate infection During menstruation, frequent urination, painful urination and pain in the pelvic area are observed. Treatment is usually with antibiotics. Early diagnosis is important. A specialist doctor should be consulted.
What are the symptoms of prostate infection?
A burning sensation or pain during urination is a common symptom because it is associated with the bladder and urinary tract. Inflammation irritates the urinary tract and can make it difficult to pass urine. This can cause the patient to hesitate to urinate. It can create a feeling of fullness in the bladder. Patients may feel the need to urinate more frequently, especially at night (nocturia). It is caused by increased pressure on the bladder caused by inflammation of the prostate. The need to urinate frequently can negatively affect daily life.
Prostate infection The prostate may swell and compress the urethra. This may cause the urine flow to weaken, become intermittent or stop completely. Patients may have difficulty urinating and may feel that the bladder is not completely empty. It may cause severe pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area. This pain may be constant. It may become more pronounced while urinating, sitting or during physical activities. In addition, discomfort may be felt around the anus. Since the area where the prostate is located causes inflammation, pain is felt in the groin area. This pain usually feels like a dull pressure and may increase over time. Pain or discomfort during ejaculation during or after sexual intercourse is one of the important symptoms. This condition occurs when the infection affects the ducts in the prostate gland.
In the case of acute prostatitis, the infection can cause a general inflammatory reaction in the body. This manifests itself with flu-like symptoms such as high fever, chills, and fatigue. These symptoms are usually seen in acute cases and require medical attention. Advanced prostate infection, can cause blood in the urine or semen. This condition occurs when the prostate ducts are damaged by inflammation. Dark urine or pink-red stains can be a significant sign. Untreated infection can lead to secondary problems with the bladder and kidneys. Incomplete emptying of the bladder can cause the infection to spread. This can lead to more serious urinary tract infections or kidney infections.
What Causes Prostate Infection?
Infections in the urinary tract can cause bacteria to reach the prostate. This is especially common in patients whose bladders cannot empty completely. Sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia and trichomoniasis can cause this. Blockage in the prostate ducts can prevent the gland from emptying. This can lead to infection. Diabetes, HIV or other conditions that suppress the immune system prostate infection Long-term use of a urinary catheter may allow bacteria to reach the prostate from the bladder.
Impact to the pelvic area, activities such as cycling, cause irritation to the prostate gland. Hormonal fluctuations can increase the risk of inflammation of the prostate gland. Symptoms include frequent and urgent urination, burning during urination, pelvic pain and sometimes high fever. If these symptoms are seen, a urologist should be consulted without delay. Appropriate treatment is usually provided with antibiotics. However, the treatment method may vary depending on the underlying cause.
How is Prostate Infection Treated?
Medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen may be prescribed to relieve pain and inflammation. Muscle relaxants may also be effective in relieving symptoms. Warm sitz baths or warm compresses may help reduce pain in the pelvic area. Alpha-blockers relax the muscles in the urinary tract. They reduce pressure on the bladder neck and make it easier to urinate. This is especially helpful for patients who have difficulty urinating. It is recommended to avoid substances that irritate the urinary tract, such as caffeine and alcohol. Drinking plenty of fluids helps prevent urinary tract infections and heal the infection.
Exercises that strengthen the pelvic floor muscles can reduce pressure on the prostate and bladder. prostate infection If an abscess has formed, surgical drainage may be required. This is usually seen in severe cases where antibiotics are not effective. In the case of non-bacterial prostatitis, no infection is detected. Therefore, treatment focuses on managing symptoms. Physical therapy, stress management and painkillers can be used. Avoiding sitting for long periods and exercising can help relieve symptoms. Treatment should always be done in consultation with a doctor. Starting treatment early is important to prevent complications and speed up the healing process.