Prostate cancer
It is among the most common types of cancer. Among the most common types of cancer in men prostate cancer It progresses in a very insidious way. Prostate cancer can be defined as prostate cancer when some cells formed in the prostate tissue show an abnormal course and turn into malignant tumors that usually start from the outer shell of the prostate and spread.
Some prostate tumors remain in their area and do not spread to other organs. These are called benign tumors. Some prostate tumors spread to other organs. These are called malignant tumors. These malignant tumors are also called cancer.
The disease affects one in every nine men worldwide. The average age at which this cancer occurs is 66. Prostate cancer Since it is the most common type of cancer in men, every man should have a routine prostate examination. If the disease is detected early, the chance of success in treatment is high.
What is Benign Prostate Enlargement?
The prostate, which is part of the male reproductive system, is responsible for producing the fluid that protects sperm and preventing urinary incontinence by storing sperm in a healthy way. The prostate gland grows due to aging. This growth is usually observed in the transition area surrounding the urinary tract. The prostate may enlarge and affect the bladder or urethra, obstructing the flow of urine. In this case, symptoms of benign prostate enlargement such as frequent, painful, bloody urine occur in men.
What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?
This insidious cancer, which does not show any symptoms in the early stages, appears with some complaints depending on the progression of the disease. Prostate cancer symptoms can be listed as follows;
- Feeling of discomfort in the groin area
- difficulty urinating
- erectile dysfunction
- Pain during ejaculation
- Blood in semen or urine
- Loss of strength in urine flow
- bone pains
The Importance of Early Diagnosis in Prostate Cancer
If the disease is diagnosed at an early stage and the cancer has not yet spread outside the prostate, it is possible to get rid of this disease thanks to early diagnosis. Therefore, it is very important for men over 50 to have a prostate check once a year.
Every man over the age of 50 should have a rectal prostate examination and have the PSA value checked in the blood at least once a year. In this way, cancer that has not yet shown symptoms and is in the early stages can be detected.
Even in his family prostate cancer Those with the disease, black men, and men with the BRCA2 gene + should start cancer screening after the age of 45. Thanks to improved prostate cancer screenings, the number of men dying from this type of cancer has decreased significantly in the last 20 years.
Causes and Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer
Although it is not known exactly why the disease occurs, there are causes and risk factors for prostate cancer. Prostate cancer occurs as a result of uncontrolled growth of prostate cells due to genetic defects at the cellular level and replacing healthy cells. Although we cannot list the exact causes, there are several definite risk factors in prostate cancer;
- Age (The risk of prostate cancer increases significantly with age.)
- Race (The risk of prostate cancer is quite high in black people in America.)
- Genetics (The risk is higher in those with a family history of prostate cancer, especially in a first-degree relative.)
- Nutrition (It is not clear whether nutrition plays a role, but prostate cancer is more common in men who eat protein-rich diets.)
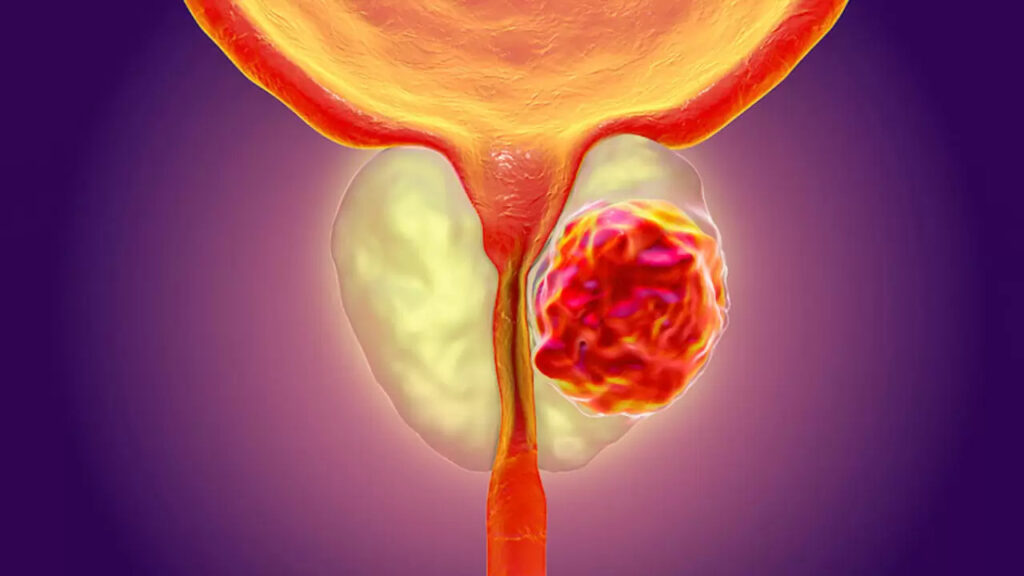
Diagnosis and Diagnosis of the Disease
In order to treat cancer, it is necessary to diagnose it at an early stage, before the cancer spreads to any part of the body. Diagnosing cancer while it is still in the prostate speeds up the treatment process.
Unfortunately, no blood test, genetic test, or any imaging method can definitively show cancer confined to the prostate in a man. Therefore, every man over the age of 50 who consults a urologist is considered a potential prostate cancer patient and some tests are performed. Prostate biopsy is performed on men who are deemed to be at risk for cancer.
Some Examinations Performed on People with Possibility of Prostate Cancer
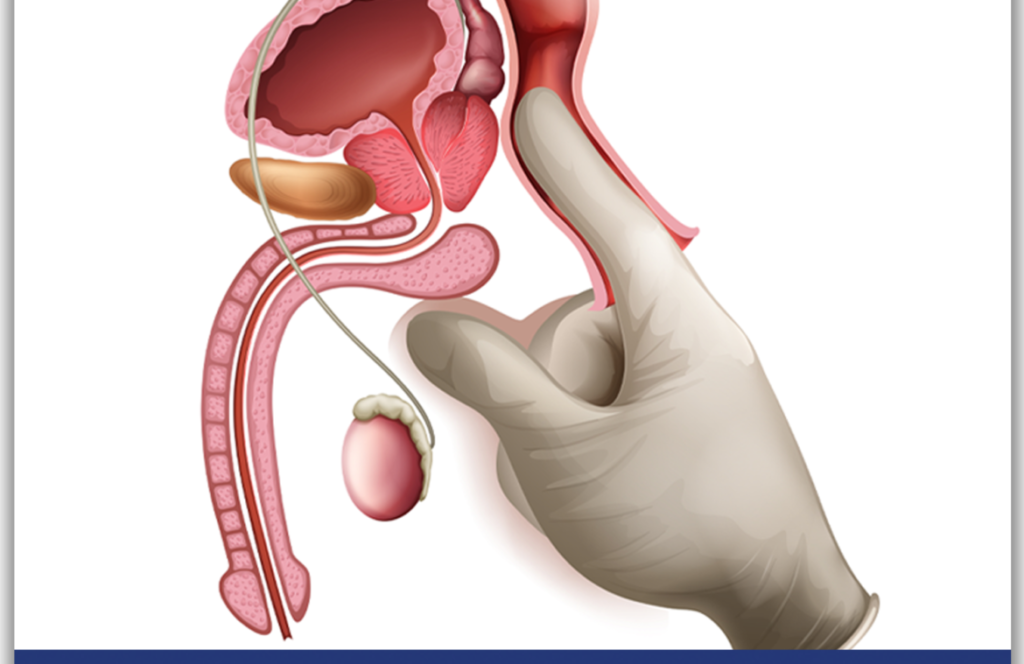
DRE (Digital Rectal Examination): The physician puts on gloves and inserts his finger into the patient's anus. Examines the size and shape of the prostate with a finger. If a hardness is felt inside the prostate, prostate cancer is suspected and the patient is recommended a prostate biopsy.
PSA (Prostate Specific Antigen): PSA is a test taken from blood. It is observed by measuring a protein produced in the prostate gland and can also be detected in the blood. PSA levels in the blood also increase in cases of cancer, infection and benign prostate enlargement. However, the PSA test does not provide a definitive diagnosis of cancer, it only shows the risk of cancer.
Prostate Cancer Gene 3 (PCA3): İdrardan bakılan genetik tabanlı bir testtir. Prostat masajı sonrası alınan idrardan PCA3 bakılmasına dayanan bir testtir. Ancak PSA’sı yüksek olan bir kişide PCA3 testi negatif gelirse, o kişide %91 oranında kanser yoktur.
Stages of Prostate Cancer
After prostate cancer is diagnosed, cancer staging is performed to plan treatment. The Urologist uses the results of the tests applied to the patient to determine the stage of the cancer and how far the tumor has progressed. The TNM staging system is used to determine the stages of the disease.
T: Describes the size and location of the tumor and how deep it is in the tissue.
N: Indicates whether cancer cells have spread to the lymph nodes or the channels connecting the lymph nodes.
M: Indicates whether cancer cells have spread to distant organs or tissues.
- Stage: In the first stage of cancer, the tumor is only on one side of the prostate. Cancer usually grows slowly. The PSA level is low and tumor cells may not be felt during DRE.
- Stage: Cancer may be on one or both sides of the prostate gland. PSA blood test is below 20. Gleason score is 7 – 8.
- Stage: Cancer progresses locally. Gleason score and PSA are high. For this reason, the probability of cancer spreading is high.
- Stage: In the final stage of the disease, the tumor has spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body.

Prostate Cancer Treatment
There are different treatment options for the treatment of cancer. Which treatment method is suitable for the patient is decided by the doctor after examination and clinical tests. However, it is widely preferred prostate cancer treatment applications include:
Active Monitoring: In addition to PSA and DRE tests, the patient is actively monitored with regular prostate biopsies. In the active surveillance method, the development of prostate cancer is followed. If the cancer grows, other treatment options are applied.
Prostate Cancer Surgery: It is a surgical method used to completely remove prostate cancer from the body. It is called prostatectomy. During surgery, the prostate and surrounding tissue are removed.
The treatment method performed with the Da Vinci robotic surgery robot to remove cancerous tissue in the prostate is called robotic radical prostatectomy. Robotic prostatectomy provides improvements in prostate cancer surgery with very high success rates. This surgery can also be performed laparoscopically and openly.
Radiation Therapy: High energy is used to kill cancer cells. There are two different types of radiation treatments. In the external radiation therapy option, radiation is detected and directed to cancer cells by a machine outside the body. In the internal radiation therapy option, radioactive seeds are surgically placed in or near the cancer to destroy cancer cells.
Other treatment methods used in the treatment of prostate cancer, whose clinical research is ongoing, are as follows:
Cryotherapy: Inserting a special catheter into the prostate cancer to freeze and kill the cancer cells.
Chemotherapy: A treatment method that uses special drugs to shrink or kill cancer.
High Intensity Focused Ultrasound: This therapy directs high-energy sound waves, or ultrasound, at the cancer to kill cancer cells.
Hormone Therapy: This method prevents cancer cells from receiving the hormones they need to grow. In this way, it is aimed to stop cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions
The first symptoms of prostate cancer, which is common in men, appear with difficulty urinating. Symptoms such as frequent urination and blood in the urine or semen are also among the symptoms of prostate cancer.
Abdominal pain and chronic pelvic pain may occur in patients with prostate cancer.
Cancer can develop in the prostate tissue in all men. For this reason, it is very important to perform annual checks.
After surgery performed as a result of prostate enlargement, the patient can have sexual intercourse.
Prostate cancer, which usually progresses slowly, can sometimes grow more quickly and in some cases spread to other parts of the body.
Our treatments
- Prostate cancer
- Bladder Cancer
- Kidney Cancer
- Kidney stone
- Robotic Surgery
- HOLEP
- ThuLEP
- Prostate Biopsy
- hydrocele
- Varioxel
- Testicular Cancer
- Urinary tract infection
- Urinary Incontinence in Women
- Urodynamics
- Vesicovaginal Fistula
- Laparoscopy Surgery
- Sacral Neuromodulation
- Laser Prostate Surgery
- Penile Prosthesis Implantation
- Prostate Hot Water Steam Treatment
- Penile Shock Wave Therapy – ESWT
- Male Infertility
- Drug Treatment for Sexual Dysfunction (Erectile Dysfunction)


