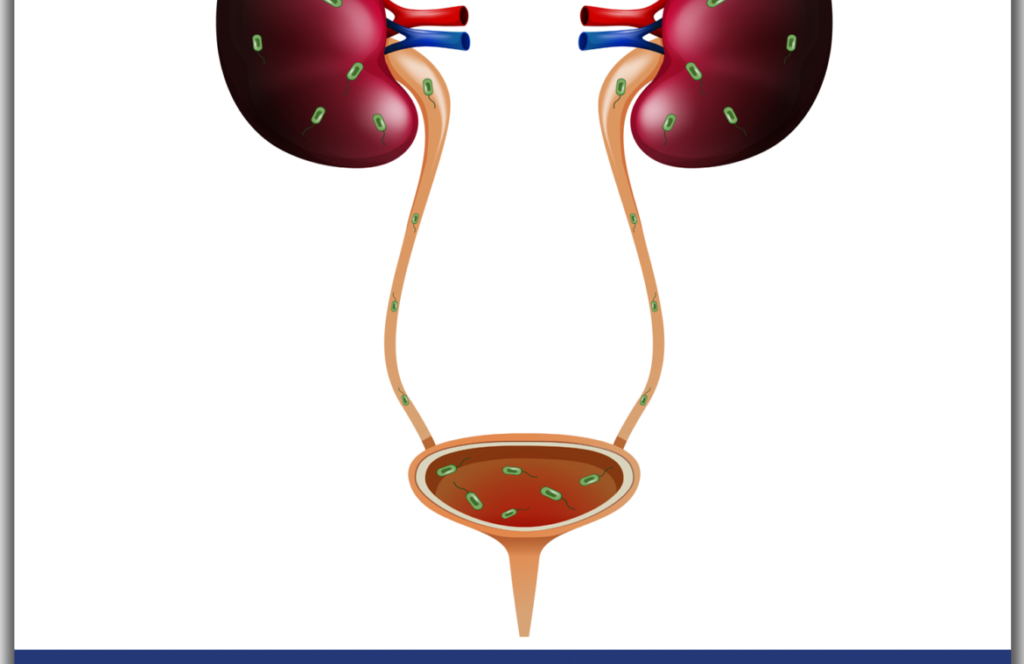
Urinary tract infection
Almost everyone has it at least once urinary tract infection has been seen. The main cause of this disease is infection of the urinary tract organs, namely the kidney, ureter, bladder and urethra. It is a disease that progresses differently in different age, gender and patient groups.
Urinary Tract Infection disease is seen in all ages and genders. Urinary tract infection is most commonly seen when the bladder organ becomes inflamed or infected. The urinary tract, which normally does not contain any bacteria, can cause serious infections with a very small number of bacteria.
Urinary tract infection It may occur in the same way in everyone and may not show the same symptoms. The patient's immune system affects the course of these infections. In some cases, it may be mild, while in other cases, it may present with very severe complaints. Urinary tract infections are very common, especially during pregnancy.
What is Urinary Tract Infection Disorder?
Urinary system; Urinary tract infection is caused by infection with bacteria, fungi or viruses. Urinary tract infection disease frequently occurs with symptoms such as urination, blood in the urine, burning or pain. It is seen in women, children and men. seen in women urinary tract infection It is seen in infections of the kidney and upper urinary tract, as well as in the lower urinary tract and bladder. The reason for this disorder, which is more common in women, is that the length of the urethra is shorter than in men. Another reason is that the distance between the anus and the urethra is short.
Urinary tract infection in men is rarer than in women. It is due to the antibacterial properties in the prostate fluid and the dry environment around the urethra that prevents the growth of bacteria. Circumcision in men also makes this a rare disorder. Symptoms of urinary tract infection are urinary frequency, burning sensation while urinating, and pain in the lower groin. Other symptoms include fever, chills and chills.
How Does Urinary Tract Infectious Disease Occur?
Urinary tract infection can cause very serious diseases in children, the elderly and pregnant women. The disease may not cause any symptoms in people with normal immune systems. Having inflammatory cells in the urine does not always mean there is an infection. With urine culture and sensitivity tests, it can be learned which bacteria in the urine causes the infection and which antibiotic treatment it responds to. Urinary catheter is also among the factors that cause urinary tract infection. The residence time of the catheter affects the occurrence of infection. Especially in women, the elderly, and patients with diabetes, catheters may cause urinary tract infections if hygiene is not observed during catheter placement.
Urinary Tract Infection in Women
Cystitis occurring in the lower urinary tract or bladder and infections occurring in the kidney or upper urinary tract are among the urinary tract infections. This condition, which is more common in women, is caused by the fact that the length of the urethra is anatomically shorter than in men. For this reason, bacteria rise to the top more easily. Bacteria that reach the bladder cause cystitis, and bacteria that reach the kidney cause pyelonephritis. One of the common reasons for urinary tract infection in women is due to the short distance between the anus and the urethra.
Urinary Tract Infection in Men
Especially in men between the ages of 15 and 50 urinary tract infection It is rare. Bacterial growth is less common due to the antibacterial content in the prostate fluid and the dryness of the urethra environment. The risk of simple cystitis is higher in men who are not circumcised. The risk of urinary tract infection is higher in cases of structural or functional urinary tract abnormalities, neutropenia, or immunosuppression.
Types of Urinary Tract Infection Disorder
- Cystitis: Infections in the bladder or urethra.
- Pyelonephritis: Infections in the upper urinary tract or kidneys.
- Simple Urinary Tract Infection: It is usually managed on an outpatient basis and treated with antibiotics.
- Complicated Urinary Tract Infection: It is a condition in which the patient presents with serious complaints and requires hospital treatment.
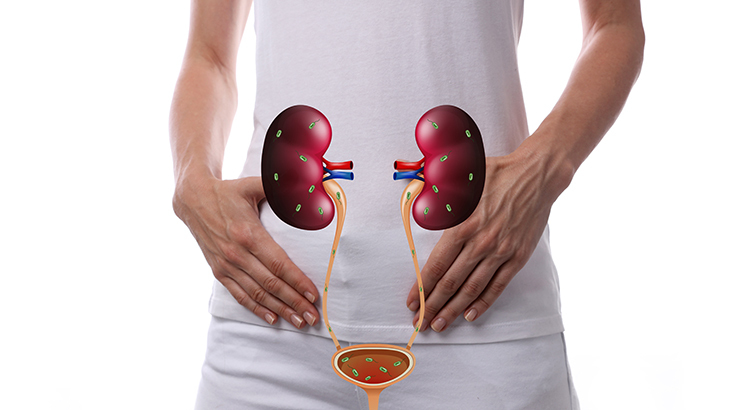
How is Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosed?
To diagnose urinary tract infection, the patient is asked to perform tests such as urine analysis and culture analysis. Complicated urinary tract infection In people with this condition, urinalysis and microscopic urine examination are performed. Bacterial formation is observed in the urine culture test. The diagnosis is confirmed and sensitivity testing is performed to initiate appropriate antibiotic treatment. In some cases, the results of the urine culture test may take a long time, so antibiotic treatment is started immediately. Depending on the urine culture result, the type of antibiotic may be changed.
What are the Treatment Methods for Urinary Tract Infection?
To be applied to the patient urinary tract infection treatment may vary depending on the degree of the disease. Antibiotics are one of the first-line treatments for urinary tract infections. Antibiotics to be used in the treatment of simple cystitis and antibiotic treatments to be used in complicated infections may differ. If the patient's condition is more severe, he may be hospitalized for treatment and follow-up.
What Should Be Done to Reduce the Risk of Urinary Tract Infection?
- Water consumption should be increased,
- Urinary retention should be avoided,
- Cleaning after using the toilet should be done from front to back.
- The genital area should be cleaned before and after sexual intercourse.
- The use of soap should be avoided when cleaning the genital area.
- Hygienic pads should be changed frequently,
- Cotton underwear should be worn.
Frequently Asked Questions
The main reason behind urinary tract infection is often known as infection caused by bacteria.
The treatment method may vary depending on the stage of the disease. Generally, in healthy women, a urinary tract infection can last an average of six days.
People with urinary tract infections need to wash their bladder regularly by drinking plenty of water. Additionally, consumption of herbal teas is also good for urinary tract infections.
Our treatments
- Prostate cancer
- Bladder Cancer
- Kidney Cancer
- Kidney stone
- Robotic Surgery
- HOLEP
- ThuLEP
- Prostate Biopsy
- hydrocele
- varicocele
- Testicular Cancer
- Urinary tract infection
- Urinary Incontinence in Women
- Urodynamics
- Vesicovaginal Fistula
- Laparoscopy Surgery
- Sacral Neuromodulation
- Laser Prostate Surgery
- Penile Prosthesis Implantation
- Prostate Hot Water Steam Treatment
- Penile Shock Wave Therapy – ESWT
- Male Infertility
- Drug Treatment for Sexual Dysfunction (Erectile Dysfunction)
