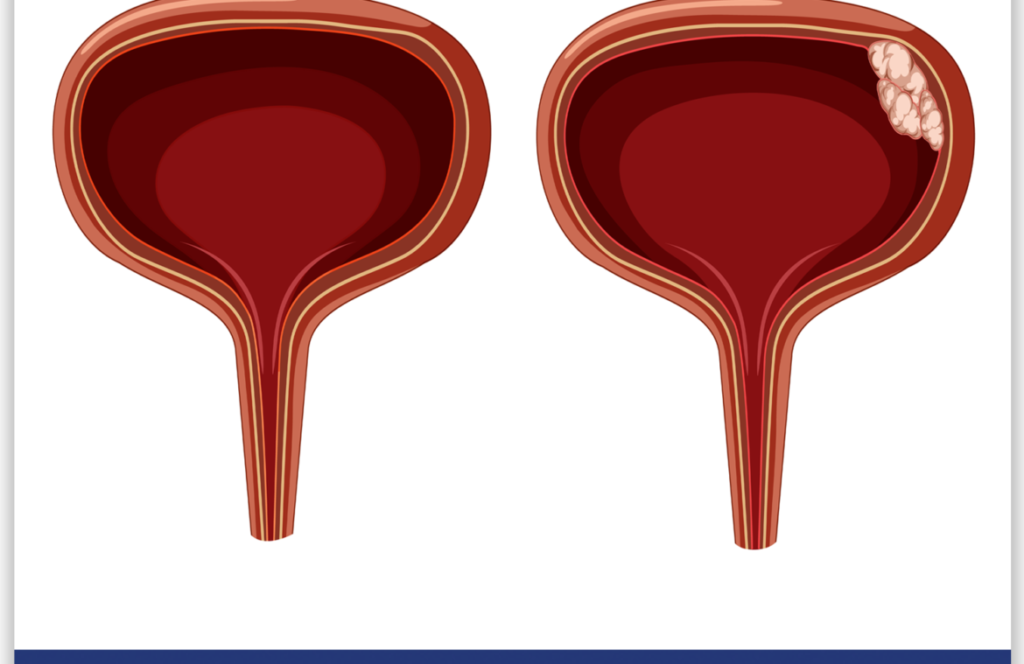
Bladder Cancer
Although it is less common in women, it is among the most common cancers in men. bladder cancer is located. This type of cancer, which is one of the most common types of cancer in the world, can be seen in all age groups. The age group where the disease is most common is known to be after 60-70.
The disease occurs due to the formation of malignant tumors in the urothelial cells of the mucosa on the inner surface of the bladder. Bladder tumors can be benign or malignant. Although bladder tumors usually occur in the bladder, they can also occur in other parts of the excretory system. bladder cancer symptoms It arises with various complaints.
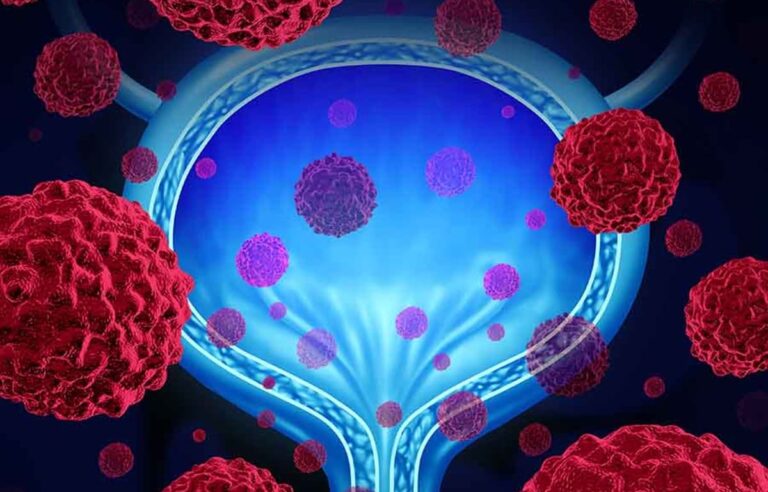
Bladder Cancer Symptoms
The bladder is a hollow muscular organ located in our lower abdomen that stores urine. A bladder tumor occurs as a result of the proliferation of cancer cells in the cells on the inner surface. The most common symptom of a bladder tumor is blood in the urine. Bladder cancer symptoms can be listed as follows;
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Feeling of urgency in urination,
- Feeling of going to the toilet frequently,
- Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder,
- Feeling of straining while urinating,
- Feeling pain while urinating
Listed symptoms bladder cancer symptoms It is located between. However, these symptoms are not sufficient to directly diagnose bladder cancer. Symptoms may also be caused by different problems. For this reason, in order to make a definitive diagnosis, the patient must consult a urologist and some tests must be performed on the patient.
Bladder Tumor
Squamous Epithelial Cell Carcinoma: Cancer arises from squamous epithelial cells that develop in the bladder after the bladder is exposed to long-term infection and irritation. Approximately %6-8 of bladder tumors consist of this type of cancer.
Adenocarcinoma: It originates from the glandular cells in the bladder. %2 of bladder tumor is this type of cancer.
Transitional Epithelial Cell Carcinoma (THC): It is the most common cancer in the bladder. Cancer arises from the epithelial cells lining the inner surface of the bladder. The progression of cancer occurs when it spreads to the muscle layer beneath the epithelial cells. The tumor then reaches the outer wall of the bladder and spreads into the fatty tissue around the bladder. This condition is defined as invasive bladder cancer.
Bladder What are the causes of cancer?
Caused by the proliferation of bladder cancer cells bladder cancer It may occur as a result of various risk factors. Factors that affect the development of the disease include smoking, advancing age, exposure to chemicals, previous cancer treatment, chronic bladder inflammation and genetic factors.
- To smoke: Smoking causes chemical accumulation in urine. This may increase the risk of cancer.
- Advancing Age: The risk of cancer increases with advancing age. Cancer can occur at any age, but the risk of cancer is lower in patients under the age of 40.
- Being a Man: Men are more likely to develop bladder tumors than women.
- Chemical Exposure: It is thought that the accumulation of harmful chemicals in the blood in the bladder increases the risk of bladder cancer. Arsenic, chemicals used in paint, rubber and leather manufacturing carry cancer risk.
- Previous Cancer Treatment: Having previously received cancer treatment increases the risk of cancer.
- Chronic Bladder Inflammation: Long-term use of a urinary catheter increases the risk of tumor formation in the bladder. Recurrent urinary infections and inflammations can also increase the risk of bladder cancer.
- Personal or Family History of Cancer: People who have had a bladder tumor before have a high risk of developing cancer again. People with a history of cancer in their first-degree relatives also have a risk of bladder tumors.
Bladder Cancer Diagnosis
In order for the patient to be diagnosed with bladder cancer, various tests and procedures must be performed by the physician. Following the general examination, cystoscopy is performed to examine the inside of the urethra and bladder. During cystoscopy, a biopsy is performed with a special tool. A urine sample is taken from the patient and analyzed under a microscope. Tomography or MRI scans are performed to take a detailed look at the patient's upper urinary tract.
Cystoscopy: The urologist inserts a small, narrow tube into the urethra. The physician examines the disease by seeing the inside of the urethra and bladder through the cystoscope.
Biopsy: A special tool is used for biopsy examination during cystoscopy. In some cases, this procedure is also called transurethral resection of the bladder tumor.
Urine Cytology: It is the collection of a urine sample from the patient through a procedure known as urine cytology. The urine sample is analyzed under a microscope.
Imaging Tests: Within the scope of imaging tests, computerized tomography (CT), urogram and retrograde pyelogram tests are performed on the patient. With these imaging technologies, the patient's urinary tract structure is examined.
Retrograde Pyelogram: It is an X-ray examination used to take a detailed look at the patient's upper urinary tract. Dye is injected into the ureters by passing a thin tube into the urethra and bladder. The dye is then transferred to the x-ray and X-ray images are captured.
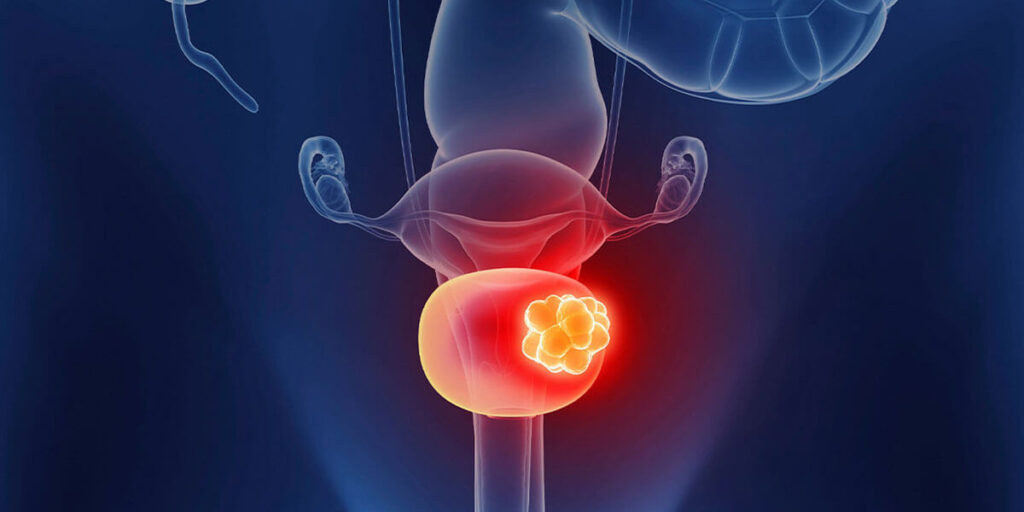
Bladder Cancer Stages
Bladder tumor stages are determined depending on the results of tests performed by the urologist, physical examinations, biopsy and imaging tests. According to the TNM classification, there are 4 main stages of bladder cancer.
- Stage: In the first stage of the disease, the cancer has spread to the subepithelial tissue, a lower layer of the epithelial layer. At this stage, there is no transition to the muscle layer.
- Stage: Cancer has advanced to the muscle layer. The disease has not spread to lymph nodes or distant organs.
- Stage: Bladder cancer has spread to the fatty layer deep within the muscles or to surrounding organs.
- Stage: Cancer has spread to distant lymph nodes. Illness; It has metastasized to organs such as lung, liver and bone.
Bladder Cancer Treatment
Today bladder cancer treatment More than one method can be applied. The physician decides the correct treatment to be applied in the light of the tests performed after the examination of the patient. Bladder cancer surgery, which is among the methods to be applied, is the method of removing and cleaning cancerous cells through a surgical operation.
Another treatment method to be applied to the patient is to apply chemotherapy only to the patient's bladder. In addition, removing the diseased bladder and making an artificial bladder to expel urine from the body is one of the treatment methods that can be preferred when necessary.
Bladder Cancer Surgery: Cancerous cells are removed or cleaned through surgery.
Intravesical Chemotherapy: It is the method of applying chemotherapy to the patient's bladder. It is preferred in cases where the disease recurs or progresses to an advanced stage.
Artificial Bladder: It is the removal of the diseased bladder and the removal of urine from the body.
Systemic Chemotherapy: It is the application of chemotherapy to the patient's entire body.
Immunotherapy: It is a treatment method that aims to trigger the immune system.
Radiation Therapy: It is preferred in cases where surgery is not an option.

Bladder Cancer Surgery
Transurethral Resection (TUR) surgery is the most well-known bladder tumor surgery. After detection of the tumor by cystoscopy, TUR bladder surgery is performed by entering through the urinary tract. In bladder tumors, the TUR method is generally preferred in the early stages. TUR surgery is preferred for bladder tumors that do not metastasize and spread to the muscles. The entire cancerous mass is removed by entering the urinary tract with a camera and a scraping knife.
Bladder Tumor Surgery with Radical Cystectomy
It is a surgical operation to remove the entire bladder. Radical cystectomy also includes removal of the prostate and seminal vesicles in male patients. In women, radical cystectomy is the removal of the uterus, ovaries, and part of the vagina. Following this, either an ileal conduti or an ileal artificial bladder is made for the patient using the ileum bowel segment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Bladder cancer can spread to the muscle layer of the bladder wall, the fatty tissue around the bladder, and organs such as the prostate or vagina. It can also spread to distant organs such as bones, liver and lungs.
Bladder Cancer is treated with various treatment methods. Treatment options include surgery, radiotherapy or chemotherapy.
The likelihood of bladder cancer increases with age. Bladder cancer usually occurs after the age of 60-70.
Bladder pain usually occurs in the groin area below the belly button.
Bladder cancer can be seen as a result of ultrasonography performed upon the patient's complaints. Tomography is very important in the diagnosis of the disease. Bladder tumor diagnosis is very important in cystoscopy and pathological examination.
Our treatments
- Prostate cancer
- Bladder Cancer
- Kidney Cancer
- Kidney stone
- Robotic Surgery
- HOLEP
- ThuLEP
- Prostate Biopsy
- hydrocele
- varicocele
- Testicular Cancer
- Urinary tract infection
- Urinary Incontinence in Women
- Urodynamics
- Vesicovaginal Fistula
- Laparoscopy Surgery
- Sacral Neuromodulation
- Laser Prostate Surgery
- Penile Prosthesis Implantation
- Prostate Hot Water Steam Treatment
- Penile Shock Wave Therapy – ESWT
- Male Infertility
- Drug Treatment for Sexual Dysfunction (Erectile Dysfunction)
