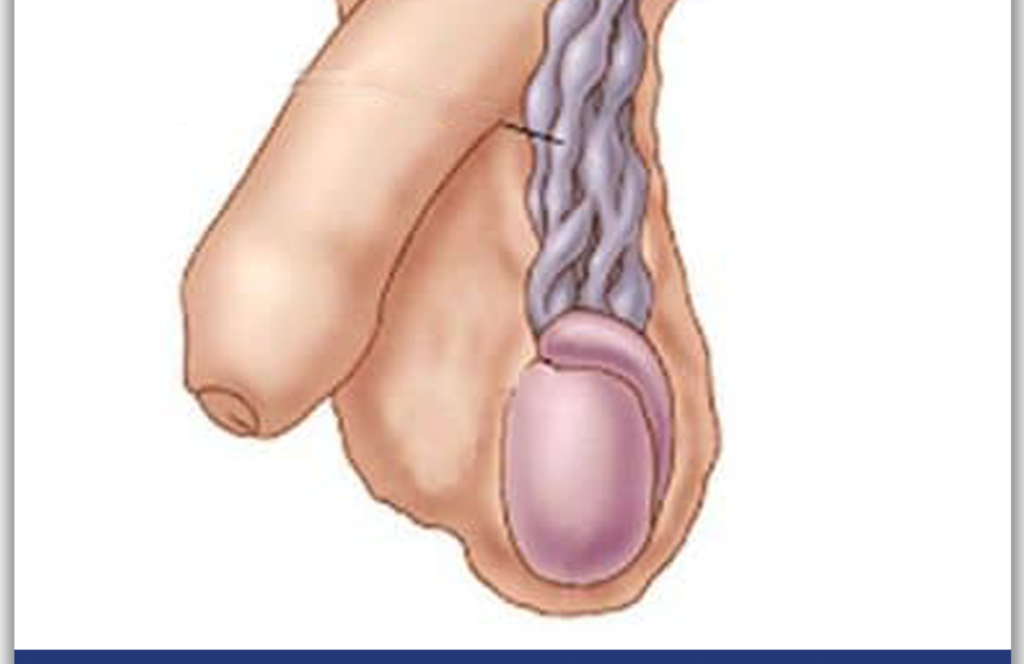
varicocele
It is a disease seen in men, caused by swelling of the veins in the scrotum. varicocele The disease can be seen at any age. This disease, which does not always show symptoms, may in some cases cause complaints such as pain, a feeling of heaviness in one of the testicles, or swelling. Additionally, the testicle with varicocele may appear larger than the other testicle.
Since varicocele can cause infertility in some patients, health institutions should be consulted if any symptoms occur. varicocele Although the diagnosis is made as a result of an examination by physicians, it can sometimes be observed on ultrasound.
Patients diagnosed with varicocele often do not require treatment. If swelling in the testicle causes pain, painkillers are used. Although rare, surgery may be performed in some varicocele patients to prevent blood flow to the swollen veins for treatment purposes.

What is Varicocele Disease?
The most common explanation for varicocele is the excessive swelling of the veins in the scrotum. Sometimes it can be understood by the appearance of varicose-like veins on the legs, which are also visible from the outside. It is a disease usually seen in adolescence and before. The disorder, which is rare in young children, begins to be seen rarely in boys in adolescence.
Varicocele disease is painless and usually does not require treatment. However, in case of pain, the testicles shrink and if they do not develop, it can lead to infertility, so a surgical operation or treatment may be required. This situation is rare.
Varicocele is usually seen in the left testicle. It causes temperature to rise or blood flow to decrease in the testicles. This may cause low sperm count and the formation of unhealthy sperm. Therefore, the patient may be infertile. And with early treatment, the patient's fertility status increases by producing healthy sperm.
What are the Symptoms of Varicocele Disease?
Pain and pain in the left side testicle, which is usually noticed when standing, and relief and dullness when lying down, are among the first symptoms. Increased scrotal temperature and shrinkage of the left testicle are also among the symptoms. The last and rare symptom is a decrease in fertility, that is, infertility.
seen in the left testicle Varicocele The disease can be seen in the right testicle or both testicles. However, this disorder seen in the right testicle can be a little more dangerous. Because the thickness of the vessels in the right testicle is greater than the left testicle and it is more common in people with a high probability of infertility.

Varicocele Disease Causes and Types
It is not yet clear why varicocele develops. Therefore, there is no risk factor that may affect the development of varicocele.
Varicocele is seen in 3 types.
- Grade Varicocele: Only noticeable during straining and straining.
- Grade Varicocele: Palpable without any force.
- Grade Varicocele: It is the most severe type and can be seen directly from the outside or at rest.
How to Diagnose Varicocele?
Diagnosing varicocele is generally easy. varicocele For diagnosis, the urology department of the health institution should be consulted. During the examination, urologists question the patients' complaints and learn their detailed medical history. A physical examination must be performed by a doctor to confirm the diagnosis of varicocele.
Urologists carefully examine the external genital organs during the examination. As a result of this examination, they check whether there is swelling in the veins in the scrotum. In addition, since knotting of the vessels in this area can cause serious problems, these structures are especially examined during the examination.
Since the veins in the scrotum can be felt more comfortably while standing, the examination is performed standing. During the examination, the doctor may ask the patient to strain or cough. In this way, the degree of varicocele, if any, is determined. Since varicocele can be seen in both testicles during the examination, both testicles must be examined. Additionally, the size of the two testicles is compared.
The scrotum with varicocele is usually smaller than the other. Apart from the physical examination, the diagnosis can also be confirmed by the physician by requesting an ultrasound test. During ultrasound examination, the backward flow of blood in the swollen veins in the scrotum can be seen and a definitive diagnosis is made. Having a varicocele only in the right testicle is a rare condition. Although very rare, varicocele formation on the right side can also be observed. In this case, it is important to also perform an abdominal ultrasound.

What are Varicocele Treatment Methods?
Although treatment is often not required in individuals diagnosed with varicocele, varicocele surgery can be performed, although rarely. For example; If there is a significant difference in testicular size in adolescents and young men varicocele treatment can be done.
Treatment options for varicocele surgery include surgical ligation (tying the vein) and microscopic varicocelectomy surgery. In some studies, an increase in sperm values and an improvement in the elimination of infertility were observed after varicocele surgery. Surgical ligation treatment is generally applied to painful varicoceles.
In men aged 21 and younger, testicular shrinkage is observed before varicocele treatment. For men who have entered puberty, sperm analysis is performed. If there is a shrinkage of the testicle or abnormal values in the sperm analysis, microsurgical varicocelectomy is performed. After the surgery, it is expected that the size of the shrunken testicle will reach the size of the other testicle and the infertility will be corrected.
Subclinical varicocele is the type of varicocele that is noticed by ultrasound but is not obvious on examination. However, in this case, treatment is generally not applied because surgery does not provide a significant improvement in sperm values. Even if the sperm values are normal, the current situation is checked by repeating the sperm analysis once a year.
How is Varicocele Surgery Done?
The purpose of varicocele surgery performed by urologists is to direct blood flow to normal veins and to compress or close the affected veins. Although it is a low-risk surgical operation, varicocele surgery has some risks, as in every surgery. These risks can be listed as follows;
- Fluid accumulation around the testicles,
- Recurrence of varicoceles,
- Infection,
- Vein damage
However, with microsurgical varicocelectomy surgery, these risks are quite low. At the same time, the probability of recurrence of the disease is very low.
Life After Varicocele Surgery
Today varicocele surgery There is a decrease in postoperative complications. This is due to the use of a surgical microscope during varicocele surgery, which allows the surgeon to see the treatment area better. Post-operative pain may last for several days. The doctor prescribes painkillers to the patient after the surgery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Varicocele surgery should be performed without delay if the conditions are suitable. If the disease is left untreated, it reduces the chance of having children.
Varicocele disease occurs due to the insufficiency of the valves in the veins that carry dirty blood from the testicles.
Varikosel ameliyatı testis boyutlarındaki farklılığa göre belirlenmektedir. Eğer fark %20'den fazla ise varikosel operasyonu önerilir. Varikoselin iki tarafta birden olması halinde testis boyut farkına bakılmaksızın cerrahi operasyona karar verilir.
Our treatments
- Prostate cancer
- Bladder Cancer
- Kidney Cancer
- Kidney stone
- Robotic Surgery
- HOLEP
- ThuLEP
- Prostate Biopsy
- hydrocele
- varicocele
- Testicular Cancer
- Urinary tract infection
- Urinary Incontinence in Women
- Urodynamics
- Vesicovaginal Fistula
- Laparoscopy Surgery
- Sacral Neuromodulation
- Laser Prostate Surgery
- Penile Prosthesis Implantation
- Prostate Hot Water Steam Treatment
- Penile Shock Wave Therapy – ESWT
- Male Infertility
- Drug Treatment for Sexual Dysfunction (Erectile Dysfunction)
