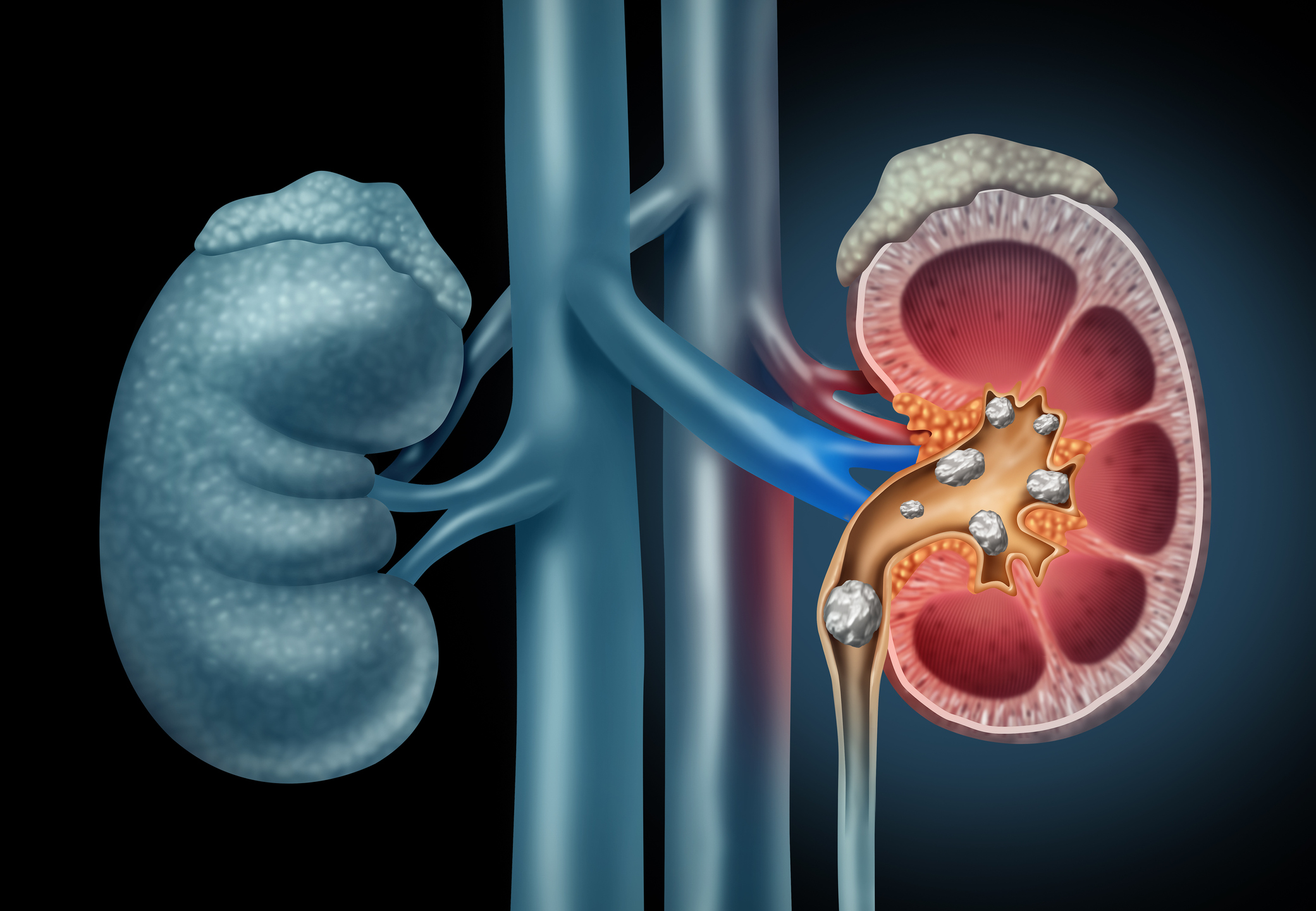
Kidney Stone Disease
It is a condition that occurs when hard mineral deposits form in the kidneys. These stones are formed as a result of an increase in the concentration of substances found in the urine. Stones can often cause pain, urinary tract obstruction and infections. Kidney stone disease, Risk factors include dehydration, genetic predisposition, and certain dietary habits. Treatment options vary depending on the size and type of stone.
Kidney Stone Disease Symptoms
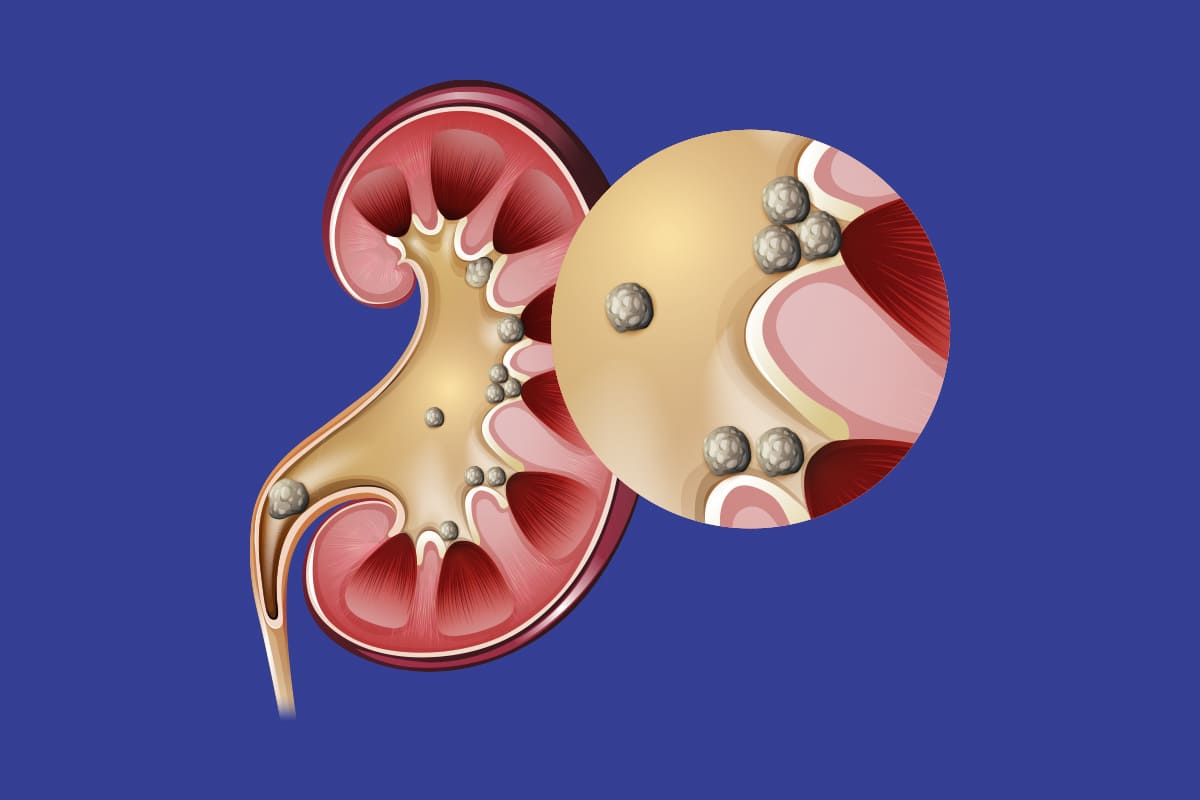
As the stone progresses in the kidneys or urinary tract, sudden and severe pain occurs in the waist and abdomen. These pains usually come and go in waves. Burning sensation during urination, frequent urination, bleeding in the urine, or cloudy and smelly urine may be observed. Kidney stone disease may cause nausea and vomiting.
Kidney stones can cause bloody urine as they move sharply through the urinary tract. You may feel a burning sensation or pain while urinating. If the stone is combined with an infection, symptoms of infection such as fever and chills may also occur. The pressure from the kidney stone may cause you to need to urinate frequently. If you have these symptoms, it is important to consult a health professional. Kidney stone disease If left untreated it can lead to serious complications.
What Causes Kidney Stone Disease?
If there is a family history of this disease, the risk of stone formation increases in the individual. Low fluid intake can cause urine to become more concentrated and minerals to crystallize more easily. Excessive intake of minerals, especially calcium, oxalate and uric acid, can increase stone formation. High salt consumption, protein-rich diets, and processed foods can trigger stone formation.
Infections that lead to the formation of kidney stones kidney stone disease It can increase the formation. Lack of movement and excess weight can increase the risk. Some medications can pave the way for stone formation. Increasing water consumption and healthy eating habits are important for preventing and treating the disease.
How is Kidney Stone Disease Treated?
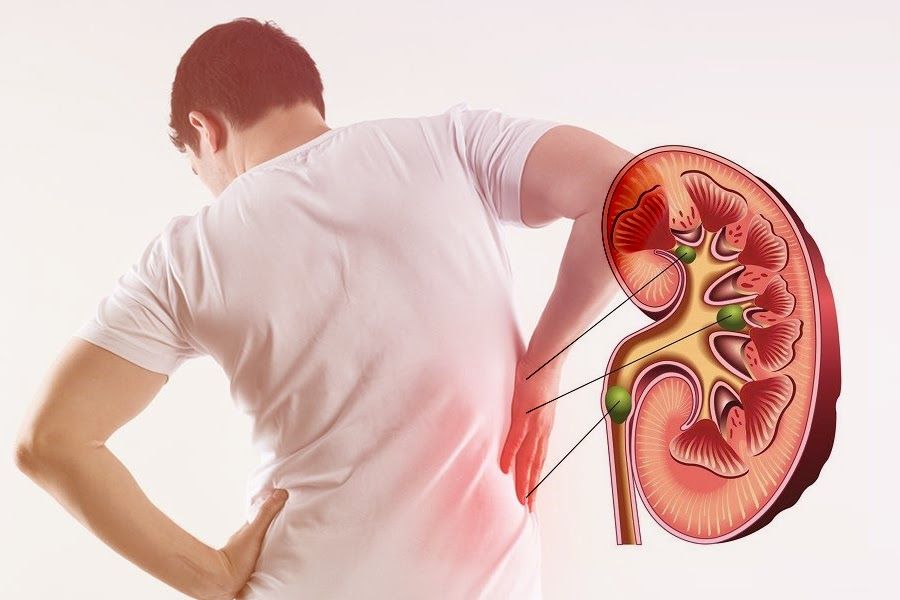
Kidney stones are usually smaller than 4 mm and can usually be passed naturally by the body. Drinking plenty of water is recommended to speed up the passage of stones from the body. Painkillers or anti-inflammatory drugs can be used to relieve pain during the stone passing process. Medications such as thiazide diuretics or potassium citrate help prevent stone formation and make the stone smaller.
One of the most common methods, ESWL, is the process of breaking stones into smaller pieces by using shock waves from outside the body. URS is the method in which stones are surgically broken or removed with a thin tube called a ureteroscope. The stones are carried to the bladder and then excreted through urine. PNL (Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy) is the method in which large kidney stones are surgically removed. The stones are intervened by entering from outside the body.
In rare cases, open surgery may be required when the stones are very large or other methods have not been successful. Kidney stone disease It is recommended to drink at least 2-3 liters of water per day to prevent recurrence. It is important to avoid foods that cause stone formation and to regulate calcium intake. Kidney stone treatment is a personal process and the most appropriate method for each patient should be determined by a urologist.