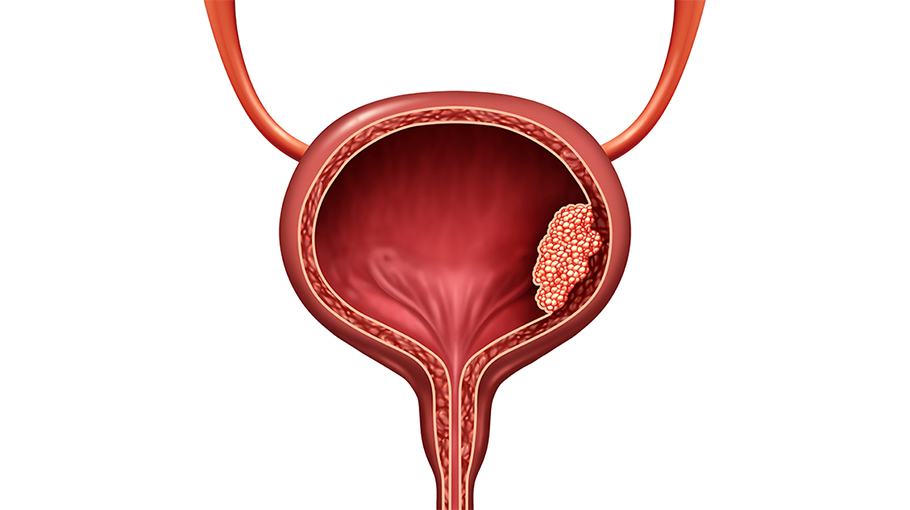
Bladder Inflammation
It is the inflammation of the inner surface of the bladder due to infection. It is usually caused by urinary tract infections. This condition manifests itself with symptoms such as painful urination, frequent urination, and cloudy or foul-smelling urine. Bladder inflammation If left untreated, it can lead to more serious health problems. Early diagnosis and treatment prevents the spread of infection.
What are the symptoms of bladder inflammation?
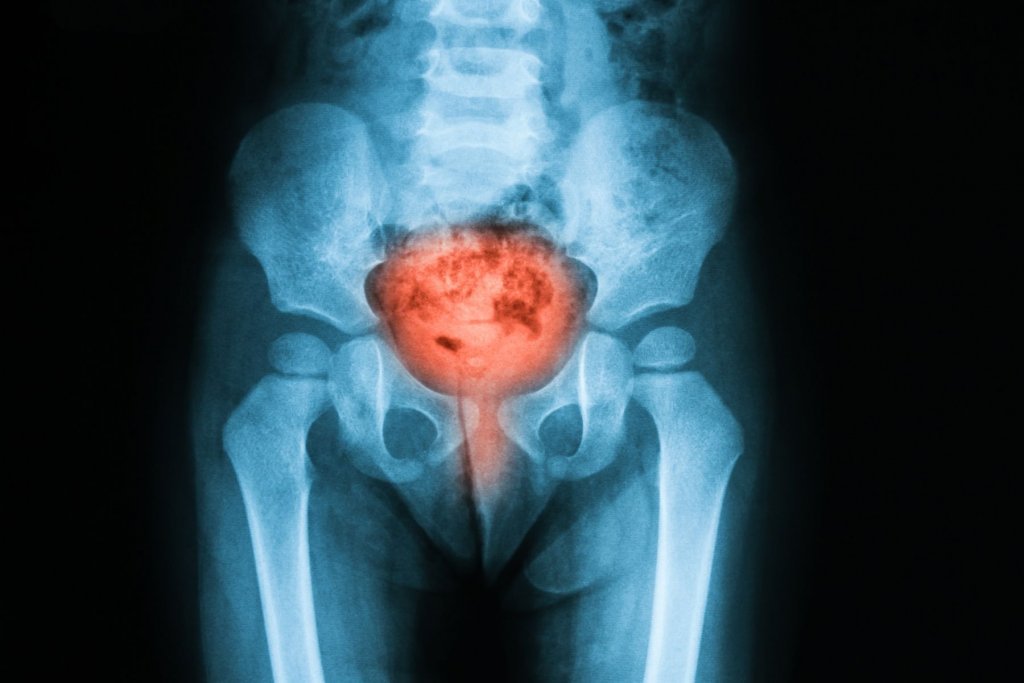
Bladder inflammation People with urethritis may feel the need to urinate frequently. However, they can only urinate small amounts each time. A burning sensation may occur during or after urination. This is a sign that the infection is affecting the bladder. Cloudy, foul-smelling, or blood in the urine may be a sign.
Pain or pressure may occur in the area where the bladder is located, especially in the lower abdomen. Pain and straining may occur during urination. This is due to discomfort caused by inflammation. In more advanced stages, the infection can spread throughout the body. This can lead to symptoms such as fever, chills, and general weakness. Sometimes it can cause a different pain or discomfort than usual when urinating. Bladder inflammation Symptoms can often get worse if not treated quickly. In this case, it is important to see a healthcare professional.
What Causes Bladder Inflammation?
The most common cause is bacteria reaching the bladder and causing an infection. It is usually caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria. Bacteria can settle in the vagina during sexual intercourse. It can reach the bladder through urine. This situation is especially common in women. Inadequate hygiene can cause bacteria to pass from the reproductive organs to the bladder. Wiping in the wrong direction after using the toilet causes bacteria to spread. Having stones in the bladder and urine not being able to drain properly from the bladder facilitates the growth of bacteria. People with weak immune systems can be infected with bacteria more easily.
Some diseases such as diabetes bladder inflammation It can cause. The risk may increase in people who have had frequent urinary tract infections in the past. Urinary tract infections may become more common in people who have a bladder catheter. Chemical substances such as soap, perfume or vaginal spray can irritate the bladder wall, which can lead to. Hormonal changes can be predisposing, especially in women who are menopausal. Treatment is usually with antibiotics. However, it is important to take preventive measures to prevent this condition from recurring.
How is Bladder Inflammation Treated?
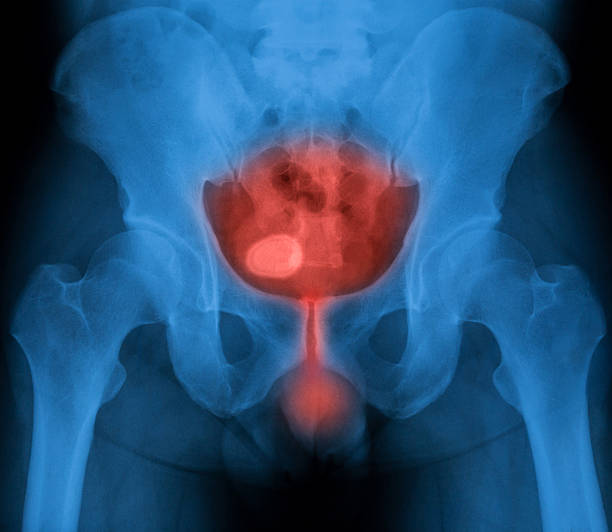
The most common treatment is antibiotics that are effective against the bacteria that cause cystitis. Your doctor will prescribe the appropriate antibiotic based on your urine culture test. This treatment usually lasts for a few days and should be continued until the infection is completely gone. Bladder inflammation Painkillers are used to relieve the pain that comes with the problem. Prescription or over-the-counter painkillers may be helpful for the burning sensation felt during urination. In addition, medications that help relax the bladder wall may be recommended.
Drinking plenty of water helps to heal urinary tract infections. Water cleans the bladder and helps to flush bacteria from the infected area. It is also recommended to avoid acidic drinks (such as acidic fruit juices). Certain dietary habits are also beneficial to prevent and heal inflammation. Foods rich in vitamin C (such as oranges, lemons, and rosehips) strengthen the immune system. In addition, avoiding sweeteners and sugar consumption protects bladder health. Bladder inflammation During the treatment process, if symptoms persist, it is important to be under medical supervision.
Usually, after the inflammation has completely gone, antibiotic treatment can be continued for a while. In addition, some lifestyle changes can be recommended to prevent urinary tract infections. In rare cases, if it becomes chronic, surgical intervention is required. However, this is usually a last resort. It is a treatable condition, but it is important to start treatment early. Methods such as antibiotic use, painkillers, increasing fluid intake and healthy nutrition play an active role in the treatment of the disease. If symptoms persist despite treatment, a doctor should definitely be consulted.